Doctorhub360.com neurological diseases encompass a wide range of disorders that affect the brain, spinal cord, and nerves throughout the body. These conditions can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, often leading to physical, emotional, and cognitive challenges. Understanding these diseases, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, is essential for effective management and improved patient outcomes.
What Are Neurological Diseases?
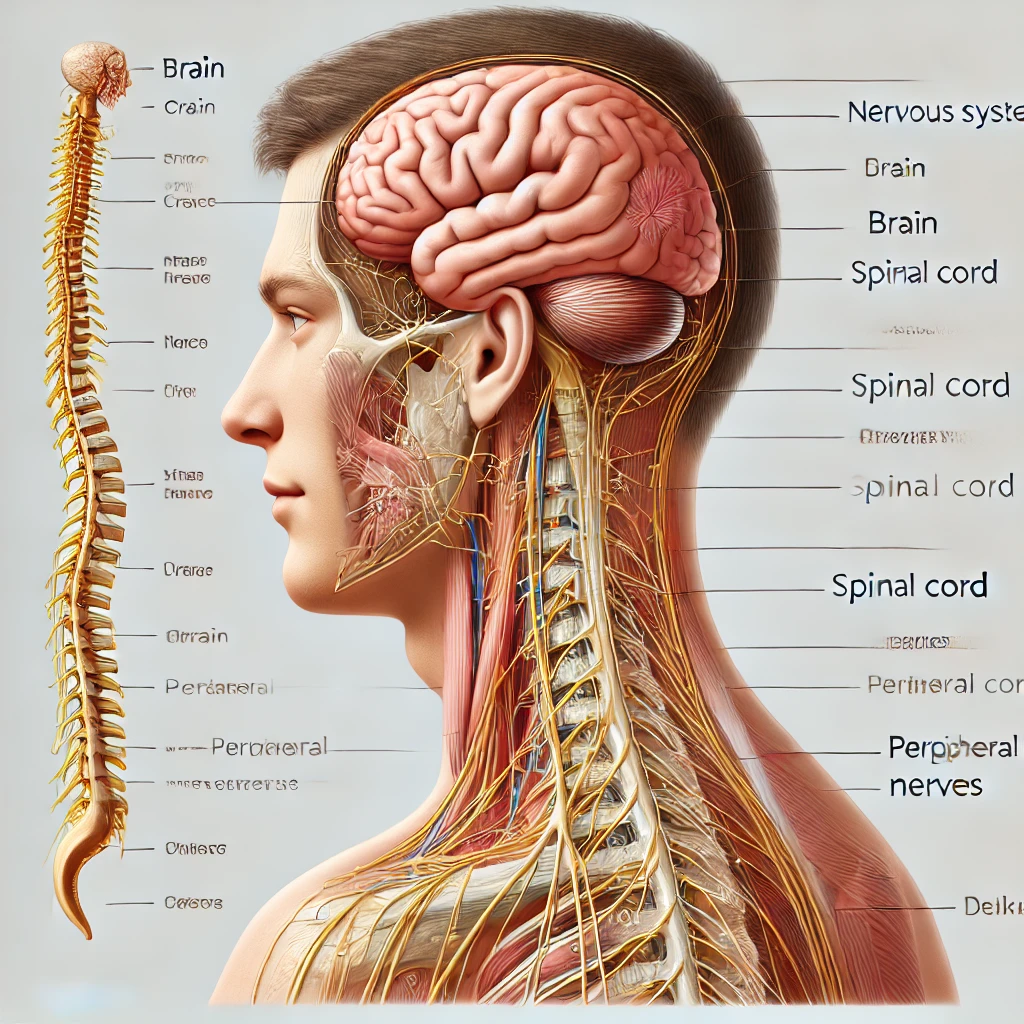
Doctorhub360.com neurological diseases refer to disorders that impair the functioning of the nervous system. This intricate system governs everything from thought processes to motor control, and even involuntary functions like breathing and heartbeat. Neurological conditions vary widely in severity and manifestation, ranging from mild headaches to life-threatening diseases such as brain tumors or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Common Causes of Neurological Diseases
Neurological diseases can arise from various factors, including:
- Genetic Predispositions: Conditions like Huntington’s disease or certain forms of epilepsy are hereditary.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections can lead to neurological issues such as meningitis or encephalitis.
- Trauma: Physical injuries to the head or spine can result in disorders like traumatic brain injury (TBI).
- Degeneration: Age-related changes may lead to degenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions such as multiple sclerosis occur when the immune system attacks the nervous system.
- Vascular Issues: Stroke and other blood flow disturbances can severely damage the brain and nervous system.
Symptoms of Neurological Diseases
The symptoms of doctorhub360.com neurological diseases are diverse, depending on the specific condition and the part of the nervous system affected. Some common signs include:
- Motor Impairments: Difficulty in movement, muscle weakness, tremors, or paralysis.
- Cognitive Challenges: Memory loss, confusion, and difficulty concentrating.
- Sensory Disturbances: Pain, tingling, numbness, or loss of sensation.
- Speech and Communication Issues: Difficulty speaking, slurred speech, or aphasia.
- Seizures: Uncontrolled electrical activity in the brain can cause convulsions or loss of consciousness.
- Autonomic Dysfunctions: Issues with involuntary body functions, such as irregular heartbeat or respiratory problems.
Types of Neurological Diseases
1. Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative conditions involve the progressive loss of nerve cells. Examples include:
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Characterized by memory loss and cognitive decline.
- Parkinson’s Disease: Marked by tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement).
- ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis): Affects motor neurons, leading to muscle weakness and atrophy.
2. Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
Epilepsy involves recurrent seizures due to abnormal brain activity. It may stem from genetic factors, head injuries, or unknown causes.
3. Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, either by a blockage (ischemic stroke) or bleeding (hemorrhagic stroke). Rapid medical intervention is crucial to minimize damage.
4. Migraines and Headaches
Chronic migraines and severe headaches can significantly impact daily functioning. These may be triggered by stress, hormonal changes, or dietary factors.
5. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
An autoimmune disorder that damages the protective sheath (myelin) covering nerves, leading to disrupted communication between the brain and the rest of the body.
6. Traumatic Brain and Spinal Cord Injuries
Injuries to the brain or spinal cord can lead to lasting neurological deficits, depending on the severity and location of the damage.
Diagnosis of Neurological Diseases
Diagnosing doctorhub360.com neurological diseases involves a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests:
- Neurological Examination: Assessing reflexes, coordination, sensation, and muscle strength.
- Imaging Tests: MRI, CT scans, and PET scans help visualize the brain and nervous system structures.
- Electrophysiological Tests: EEGs record electrical activity in the brain, while EMGs measure muscle response to nerve stimulation.
- Blood Tests: Can identify infections, autoimmune markers, or genetic conditions.
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): Analyzing cerebrospinal fluid for signs of infection or inflammation.
Treatment Options for Neurological Diseases
Treatment depends on the specific condition and its severity. Common approaches include:
1. Medications
- Antiepileptics: Manage seizures in epilepsy.
- Dopaminergic Drugs: Alleviate symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
- Immunomodulators: Reduce inflammation in multiple sclerosis.
- Pain Management: Analgesics and other medications address chronic pain.
2. Physical and Occupational Therapy
These therapies aid in regaining motor functions and adapting to daily challenges.
3. Surgical Interventions
Procedures such as deep brain stimulation (DBS) for Parkinson’s or surgical removal of brain tumors may be necessary.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
Dietary changes, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding triggers can improve quality of life.
5. Psychological Support
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and counseling help patients cope with the emotional impact of neurological diseases.
Preventing Neurological Diseases
While not all neurological conditions are preventable, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with balanced nutrition and regular exercise.
- Use protective gear to prevent head injuries.
- Manage chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes effectively.
- Avoid substance abuse and limit alcohol consumption.
- Stay updated with vaccinations to prevent infections affecting the nervous system.
Conclusion
Doctorhub360.com neurological diseases are complex and multifaceted, demanding a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management. Early detection and personalized care plans are crucial in mitigating their impact. As research advances, innovative treatments and technologies continue to provide hope for individuals living with these conditions.

![swimsuit edition [abbb] - 1.20 21 swimsuit edition - chapter](https://cryptonews.com.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/Add-a-heading-60.jpg)



